目录
背景介绍
之前我们了解了IOC初略的一个结构,这里我们开始学习一下spring是如何定位资源的。(桶子到哪里装水)
参考资料
http://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/htmlsingle/
spring 技术内幕
BeanDefition的Resource定位
我们以FileSystemXmlApplicationContext为例,看一下它的类图(图片如果不清楚,可以右键保存下来看),我们主要观察蓝色线条的部分:
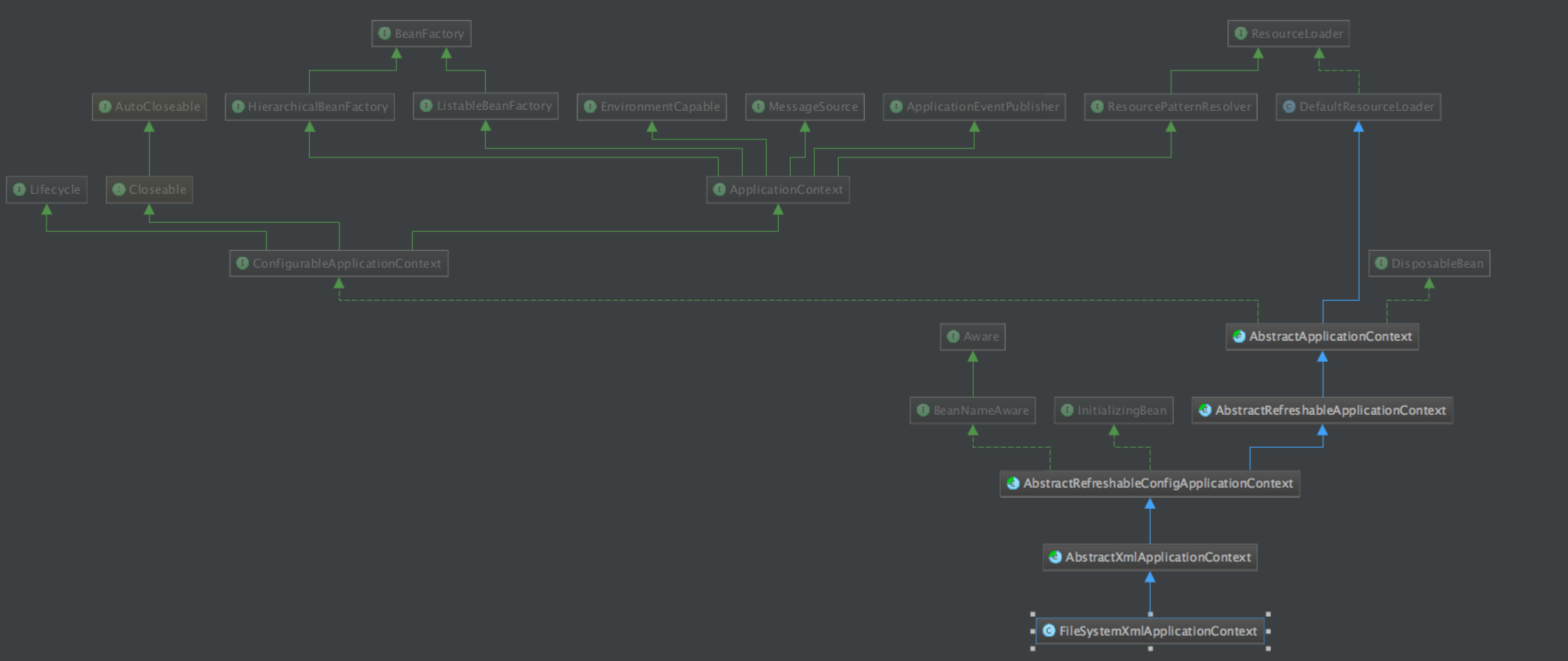
这个关系是这样的:FileSystemXmlApplicationContext --》 AbstractXmlApplicationContext --》 AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext --》 AbstractApplicationContext --》 DefaultResourceLoader
下面我们从FileSystemXmlApplicationContext代码开始看起:
容器使用的入口
//这里只贴出部分核心的代码
public class FileSystemXmlApplicationContext extends AbstractXmlApplicationContext {
//其他构造方法最终的都是调用这个方法
public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException {
super(parent);
//设置配置以及解析
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
//启动容器
refresh();
}
}
@Override
protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) {
if (path != null && path.startsWith("/")) {
path = path.substring(1);
}
return new FileSystemResource(path);
}
public void setConfigLocations(String... locations) {
if (locations != null) {
Assert.noNullElements(locations, "Config locations must not be null");
//深复制配置文件到自身属性
this.configLocations = new String[locations.length];
for (int i = 0; i < locations.length; i++) {
//挨个解析配置文件引入的占位符properties
this.configLocations[i] = resolvePath(locations[i]).trim();
}
}
else {
this.configLocations = null;
}
}
}
设置配置以及解析
//这里只贴出部分核心的代码
public abstract class AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext extends AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext
implements BeanNameAware, InitializingBean {
public void setConfigLocations(String... locations) {
if (locations != null) {
Assert.noNullElements(locations, "Config locations must not be null");
//深复制配置文件到自身属性
this.configLocations = new String[locations.length];
for (int i = 0; i < locations.length; i++) {
//挨个解析配置文件引入的占位符properties
this.configLocations[i] = resolvePath(locations[i]).trim();
}
}
else {
this.configLocations = null;
}
}
}
启动容器
//这里只贴出部分核心的代码
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader
implements ConfigurableApplicationContext, DisposableBean {
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// 为容器的启动做一些准备:设置对应状态属性。如果是web应用,同时会加载对应的属性。
prepareRefresh();
// 通知实现方去刷新内置的bean容器。前面我们讲到beanfactory的作用就是用来“装东西”的,那我们来看看这个里面的实现。
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
}
通知子类刷新内置的beanfactory
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
//步骤1:刷新beanFactory
refreshBeanFactory();
//步骤2:获得beanfactory,这里的实现很简单,直接返回xxxapplicationcontext的beanfactory的属性。beanfactory属性的设置实在步骤1完成的。
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory);
}
return beanFactory;
}
刷新内置的beanfactory具体实现
//这里只贴出部分核心的代码
public abstract class AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext {
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
//如果已经创建的bean容器
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
//清除已经创建的beans
destroyBeans();
//关闭beanfactory容器
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
//创建beanfactory,可见默认使用的beanfactory容器是这个啊。
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
//这里面设置beanfactory是否支持“bean覆盖”和“循环引用”两种选项
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//加载bean resource
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
//设置beanfactory属性
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
}
//看看容器是怎么创建的
protected DefaultListableBeanFactory createBeanFactory() {
return new DefaultListableBeanFactory(getInternalParentBeanFactory());
}
//如果双亲上下文实现了ConfigurableApplicationContext,那么返回双亲上下文的beanfactory,否则直接返回双亲上下文
protected BeanFactory getInternalParentBeanFactory() {
return (getParent() instanceof ConfigurableApplicationContext) ?
((ConfigurableApplicationContext) getParent()).getBeanFactory() : getParent();
}
资源的定位以及加载配置文件
//这里只贴出部分核心的代码
public abstract class AbstractXmlApplicationContext extends AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext {
@Override
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
// 由这里可以看到默认读取Xml的reader是这个
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
// Configure the bean definition reader with this context's
// resource loading environment.
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
//具体加载beanDefinition的方法
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
}
//我们先来看看XmlBeanDefinitionReader里面干了什么?
public XmlBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
super(registry);
}
//进入super方法看看,这个方法逻辑是根据beanFactory创建一个reader
//如果这个beanFactory不仅实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry,还实现了ResourceLoader的话,就把他设置成
//resourceloader,否则就创建一个默认的resourceloader。
//这个默认的resourceloader就是DefaultResourceLoader()。
//environment用了类似的逻辑
protected AbstractBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
this.registry = registry;
// Determine ResourceLoader to use.
if (this.registry instanceof ResourceLoader) {
this.resourceLoader = (ResourceLoader) this.registry;
}
else {
this.resourceLoader = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
}
// Inherit Environment if possible
if (this.registry instanceof EnvironmentCapable) {
this.environment = ((EnvironmentCapable) this.registry).getEnvironment();
}
else {
this.environment = new StandardEnvironment();
}
}
}